Fast Two-step Blind Optical Aberration Correction
We propose a blind method to
correct the optical aberrations caused by the point-spread
function of the lens, without any prior on the lens or the
camera to restore the image. Photograph taken with a Sony
FE 35mm f/1.8 lens at maximal aperture mounted on a
Sonyα6000 camera.
|
Abstract
The optics of any camera degrades the sharpness of photographs,
which is a key visual quality criterion. This degradation is
characterized by the point-spread function (PSF), which depends
on the wavelengths of light and is variable across the imaging
field. In this paper, we propose a two-step scheme to correct
optical aberrations in a single raw or JPEG image, i.e., without
any prior information on the camera or lens. First, we estimate
local Gaussian blur kernels for overlapping patches and sharpen
them with a non-blind deblurring technique. Based on the measurements
of the PSFs of dozens of lenses, these blur kernels are modeled as
RGB Gaussians defined by seven parameters. Second, we remove the
remaining lateral chromatic aberrations (not contemplated in the
first step) with a convolutional neural network, trained to
minimize the red/green and blue/green residual images. Experiments
on both synthetic and real images show that the combination of these
two stages yields a fast state-of-the-art blind optical aberration
compensation technique that competes with commercial non-blind algorithms.
Citation
@inproceedings{eboli22fast,
author = {Thomas Eboli and
Jean{-}Michel Morel and
Gabriele Facciolo},
title = {Fast Two-Step Blind Optical Aberration Correction},
booktitle = {European Conference on Computer Vision},
pages = {693--708},
publisher = {Springer},
year = {2022}
}
Method
The method removes the optical aberrations on the linear RGB color space (typically after
demosaicking and before color and tone manipulations). It decomposes the problem into
two simpler steps motivated by the structure of aberrations as showned in [Chang et al., TIP 2013]:
(i) we deblur the edges with a Gaussian-like blind deblurring technique to get chromatic sharper edges,
and (ii) we align with a new CNN the sharpened chromatic edges by operating on the pairs of green/red and green blue
channels to render a realistic achromatic one. The full method is ligthweight, generalizes to new images
and totally differentiable to be included in new ISP pipelines.
Results
Comparison on real JPEG images with two state-of-the-art techniques. The images are "linearized" by inversed gamma curve.

|
Original
|
Yue et al.
|
Li et al.
|
Ours
|
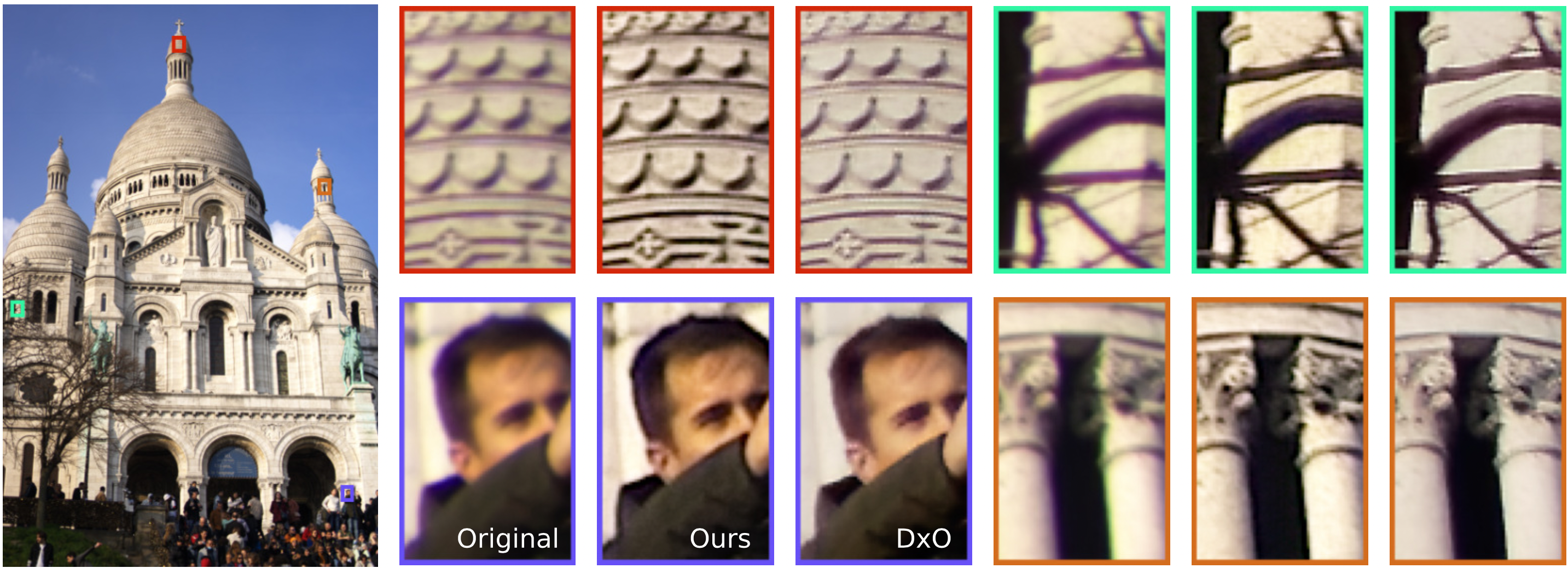
Comparisons on real raw images with the commercial solution DxO PhotoLab. The denoising and demosaicking are those
of PhotoLab. Only the aberration processing module changes.


References
- Yue et al. Blind optical aberration correction by exploring geometric and visual priors. CVPR 2015
- Li et al. Universal and flexible optical aber- ration correction using deep-prior based deconvolution. ICCV 2021
- DxO PhotoLab 5